Cloud Computing: 7 Powerful Benefits You Can’t Ignore
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses operate, offering scalable, flexible, and cost-efficient solutions for storing, managing, and processing data. Gone are the days of bulky servers and high maintenance costs—today, the cloud powers innovation across industries.
What Is Cloud Computing and How Does It Work?

At its core, cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics—over the internet. Instead of owning physical infrastructure, organizations access technology resources on-demand from cloud providers.
Defining Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is the on-demand availability of computer system resources, especially data storage and computing power, without direct active management by the user. The term “cloud” is a metaphor for the internet, symbolizing the abstracted nature of the underlying infrastructure.
- It eliminates the need for local servers or personal devices to handle applications.
- Services are delivered through a network, typically the internet.
- Users pay only for what they use, reducing operational costs.
“The cloud is not about technology. It’s about business outcomes.” — John Treadway, AWS Vice President
How Cloud Computing Works
Cloud computing operates on a shared pool of configurable computing resources hosted in data centers. These resources are delivered via virtualization technology, allowing multiple users and applications to share the same physical infrastructure securely.
- Data centers host thousands of servers managed by cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud.
- Virtual machines (VMs) simulate dedicated hardware, enabling efficient resource allocation.
- Users access services through web-based dashboards or APIs.
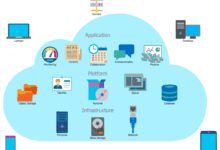
Types of Cloud Computing Services
Cloud computing is categorized into three primary service models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Each offers different levels of control, flexibility, and management.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. It’s the most basic category of cloud computing services, giving users access to networking, storage, and servers on a pay-as-you-go basis.
- Examples include AWS EC2, Google Compute Engine, and Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines.
- IaaS allows businesses to scale infrastructure up or down based on demand.
- Users manage operating systems, applications, and data, while the provider handles hardware.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS offers a platform allowing customers to develop, run, and manage applications without dealing with the underlying infrastructure. It’s ideal for developers who want to focus on coding rather than system administration.
- Popular platforms include Google App Engine, Heroku, and Microsoft Azure App Services.
- PaaS streamlines the development lifecycle with built-in tools for testing, deployment, and scaling.
- It supports multiple programming languages and frameworks.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. Users access the software via a web browser, eliminating the need for installation or maintenance.
- Common examples are Google Workspace, Microsoft 365, and Salesforce.
- SaaS reduces IT overhead and ensures automatic updates.
- It enables remote access and collaboration from any device.
Deployment Models in Cloud Computing
Cloud computing can be deployed in various ways depending on organizational needs, security requirements, and scalability goals. The four main deployment models are public, private, hybrid, and multi-cloud.
Public Cloud
In a public cloud, computing resources are owned and operated by third-party cloud service providers and delivered over the internet. These resources are shared among multiple organizations (tenants).
- Providers include AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform.
- Public clouds offer high scalability and cost efficiency.
- They are ideal for startups and businesses with variable workloads.
“The public cloud is the foundation of digital transformation.” — Satya Nadella, CEO of Microsoft
Private Cloud
A private cloud is dedicated to a single organization. It can be hosted on-premises or by a third-party provider, but the infrastructure is not shared with others.
- Private clouds offer greater control, security, and customization.
- They are commonly used by government agencies and financial institutions.
- Higher costs and maintenance requirements are trade-offs for enhanced security.
Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Models
Hybrid cloud combines public and private clouds, allowing data and applications to be shared between them. Multi-cloud involves using services from multiple cloud providers to avoid vendor lock-in and optimize performance.
- Hybrid clouds provide flexibility and help meet compliance requirements.
- Multi-cloud strategies improve resilience and reduce dependency on a single provider.
- Tools like Kubernetes and Terraform help manage hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
Key Benefits of Cloud Computing
Organizations adopt cloud computing for numerous strategic advantages. From cost savings to improved agility, the benefits are transforming how businesses innovate and compete.
Cost Efficiency and Reduced Capital Expenditure
Cloud computing eliminates the need for large upfront investments in hardware and data centers. Instead, businesses pay for what they use, turning capital expenses (CapEx) into operational expenses (OpEx).
- No need to purchase and maintain physical servers.
- Pay-as-you-go pricing models align costs with actual usage.
- Reduces energy consumption and IT staffing needs.
Scalability and Flexibility
One of the most powerful aspects of cloud computing is its ability to scale resources instantly. Whether handling traffic spikes or expanding operations, the cloud adapts in real time.
- Auto-scaling features adjust computing power based on demand.
- Global reach allows deployment in multiple regions with low latency.
- Supports agile development and rapid prototyping.
Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
Cloud computing enhances data protection and recovery capabilities. Automated backups, redundancy, and geo-replication ensure data remains safe and accessible during outages.
- Cloud providers offer robust SLAs (Service Level Agreements) for uptime.
- Disaster recovery plans can be implemented faster and at lower cost.
- Data is replicated across multiple locations to prevent loss.
Cloud Computing in Business: Real-World Applications
From small startups to Fortune 500 companies, cloud computing is driving innovation across industries. Let’s explore how different sectors leverage the cloud to improve efficiency and customer experience.
Retail and E-Commerce
Retailers use cloud computing to manage inventory, process transactions, and personalize customer experiences. During peak seasons like Black Friday, cloud scalability ensures websites remain responsive.
- Amazon uses AWS to power its global e-commerce platform.
- AI-driven recommendations are processed in the cloud.
- Cloud-based CRM systems enhance customer relationship management.
Healthcare and Telemedicine
In healthcare, cloud computing enables secure storage of electronic health records (EHRs), supports telemedicine platforms, and accelerates medical research.
- Hospitals use cloud-based systems for real-time patient monitoring.
- AI models trained in the cloud assist in diagnosing diseases.
- Compliance with HIPAA is maintained through encrypted cloud storage.
Finance and Banking
Banks and fintech companies rely on cloud computing for fraud detection, risk analysis, and digital banking services. The cloud enables faster innovation while maintaining regulatory compliance.
- JPMorgan Chase uses hybrid cloud for secure application deployment.
- Blockchain and cloud integration enhance transaction transparency.
- Real-time analytics improve credit scoring and loan processing.
Security and Compliance in Cloud Computing
Security remains a top concern for organizations moving to the cloud. While the cloud offers advanced protection mechanisms, understanding shared responsibility is crucial.
Understanding the Shared Responsibility Model
In cloud computing, security is a shared responsibility between the provider and the customer. The provider secures the infrastructure, while the customer protects data, applications, and access controls.
- AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud clearly define their security responsibilities.
- Customers must configure firewalls, encryption, and identity management properly.
- Regular audits and monitoring are essential for compliance.
Data Encryption and Identity Management
Cloud providers offer end-to-end encryption for data at rest and in transit. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) and identity access management (IAM) tools help prevent unauthorized access.
- Encryption keys can be managed by the provider or the customer (BYOK – Bring Your Own Key).
- IAM policies define who can access specific resources.
- Zero-trust security models are increasingly adopted in cloud environments.
Compliance with Regulations
Cloud computing supports compliance with global standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, SOC 2, and PCI-DSS. Providers offer compliance certifications and audit logs to help organizations meet legal requirements.
- Google Cloud provides detailed compliance documentation for enterprises.
- Automated compliance tools reduce manual effort.
- Data residency options ensure data stays within legal jurisdictions.
Challenges and Risks of Cloud Computing
Despite its advantages, cloud computing presents challenges that organizations must address to maximize benefits and minimize risks.
Vendor Lock-In
Vendor lock-in occurs when a company becomes overly dependent on a single cloud provider’s proprietary technologies, making migration difficult and costly.
- Proprietary APIs and services can limit portability.
- Solutions include adopting open standards and using multi-cloud strategies.
- Tools like Kubernetes help containerize applications for easier migration.
Latency and Performance Issues
While the cloud offers global reach, latency can affect performance, especially for real-time applications like gaming or video conferencing.
- Edge computing complements cloud by processing data closer to the source.
- Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) reduce latency for web content.
- Choosing the right region for deployment is critical for performance.
Cost Management and Optimization
Without proper oversight, cloud costs can spiral out of control due to underutilized resources or lack of monitoring.
- Unused instances and unattached storage generate unnecessary charges.
- Cloud cost management tools like AWS Cost Explorer and Azure Cost Management help track spending.
- Reserved instances and spot pricing can reduce costs by up to 70%.
The Future of Cloud Computing: Trends to Watch
Cloud computing continues to evolve, driven by advancements in AI, edge computing, and sustainability. Staying ahead of these trends is key to maintaining a competitive edge.
AI and Machine Learning Integration
Cloud platforms are becoming hubs for AI and machine learning. Providers offer pre-built models, training tools, and scalable compute power for AI workloads.
- AWS SageMaker, Google AI Platform, and Azure ML simplify model development.
- AI-powered analytics enhance decision-making across industries.
- AutoML tools enable non-experts to build machine learning models.
Edge Computing and 5G
Edge computing brings data processing closer to the source, reducing latency and bandwidth usage. Combined with 5G, it enables real-time applications like autonomous vehicles and smart cities.
- Amazon Wavelength and Azure Edge Zones integrate cloud with 5G networks.
- IoT devices generate massive data that edge computing helps manage efficiently.
- Hybrid cloud-edge architectures are becoming standard for latency-sensitive apps.
Sustainability and Green Cloud Initiatives
As environmental concerns grow, cloud providers are investing in renewable energy and energy-efficient data centers to reduce carbon footprints.
- Google Cloud aims to run on 24/7 carbon-free energy by 2030.
- Microsoft’s Azure is committed to being carbon negative by 2030.
- Efficient cooling systems and server utilization improve energy efficiency.
What is cloud computing?
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services—such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics—over the internet. It allows businesses to access technology resources on-demand without owning physical infrastructure.
What are the three main types of cloud services?
The three main types are Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). IaaS provides virtualized resources, PaaS offers development platforms, and SaaS delivers ready-to-use software applications.
Is cloud computing secure?
Yes, cloud computing can be highly secure when best practices are followed. Cloud providers implement advanced security measures, but users must also manage access controls, encryption, and compliance to protect their data.
What is the difference between public and private cloud?
A public cloud is shared among multiple organizations and managed by a third-party provider, while a private cloud is dedicated to a single organization, offering greater control and security.
How does cloud computing reduce costs?
Cloud computing reduces costs by eliminating upfront hardware investments, offering pay-as-you-go pricing, and reducing the need for on-site IT staff and maintenance.
Cloud computing has fundamentally reshaped the digital landscape, offering unprecedented flexibility, scalability, and innovation. From startups to global enterprises, organizations leverage the cloud to drive efficiency, enhance security, and accelerate growth. As technology evolves, trends like AI integration, edge computing, and sustainable practices will further expand the cloud’s potential. Understanding its models, benefits, and challenges is essential for any business aiming to thrive in the digital age.
Further Reading: